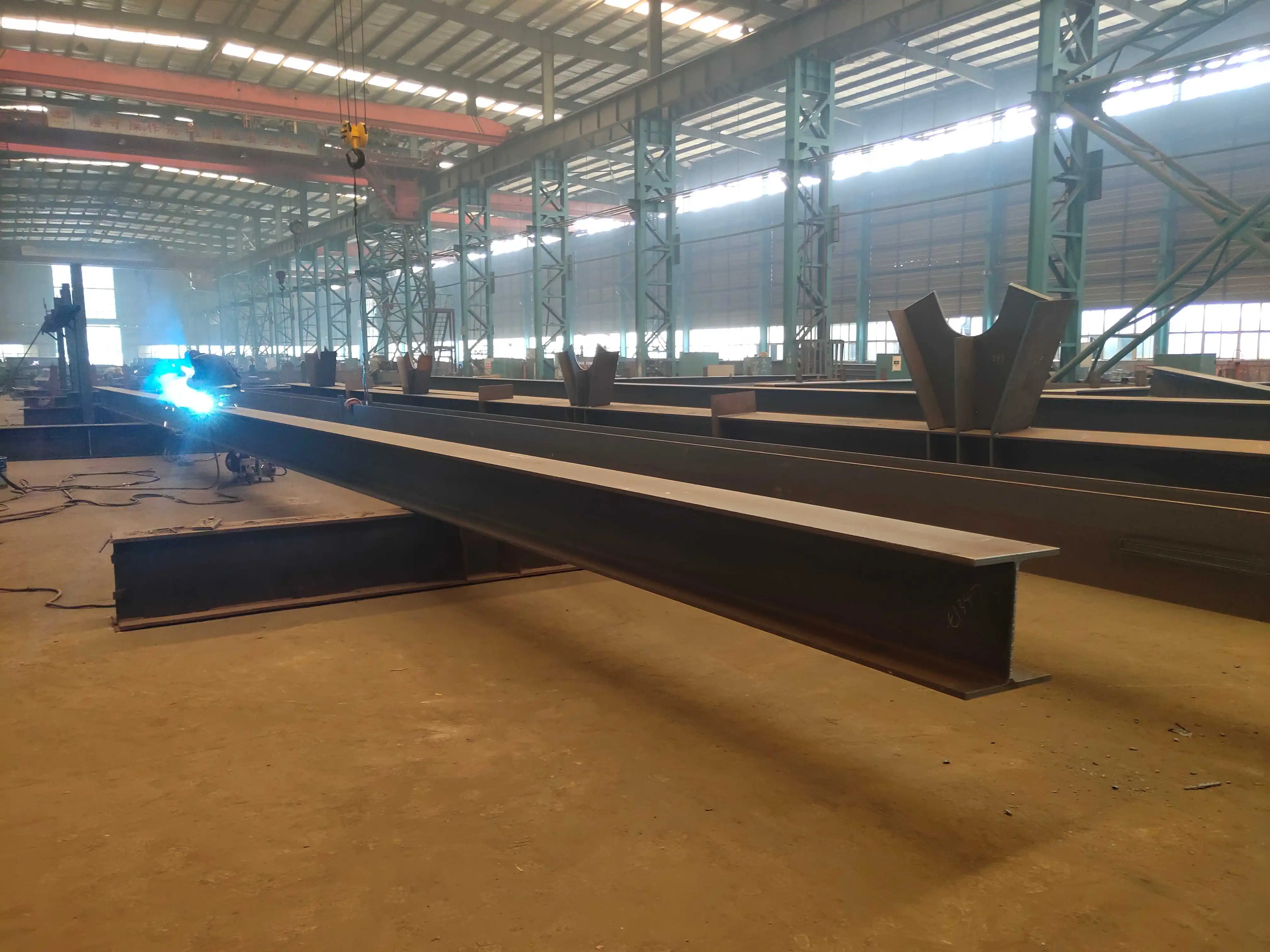
How to Prevent Corrosion and Deformation of H-Section Plate Girders in Hot and Humid Environments?
Preventing corrosion and deformation of H-section plate girders in hot and humid environments requires a multi-faceted approach. Key strategies include using advanced surface treatments like hot-dip galvanization or epoxy coatings to enhance corrosion resistance. Optimizing the steel composition by adding elements like copper and chromium improves weather resistance. Structural design plays a crucial role, with prestressing techniques minimizing temperature-induced deformation and box-section designs enhancing overall stability. These methods, combined with regular maintenance and environmental control measures, significantly extend the lifespan and performance of H-section plate girders in challenging climates.
Advanced Corrosion Protection Techniques for H-Section Plate Girders
Hot-Dip Galvanization: A Proven Shield Against Corrosion
Hot-dip galvanization stands out as a premier method for protecting H-section plate girders from corrosion in hot and humid environments. This process involves immersing the steel structure in molten zinc, creating a metallurgically bonded coating that acts as a formidable barrier against moisture and corrosive elements. The zinc layer not only provides physical protection but also offers cathodic protection, sacrificing itself to prevent the underlying steel from corroding. For H-section plate girders exposed to particularly aggressive environments, a duplex system combining galvanization with an additional layer of powder coating can offer enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal.
Innovative Epoxy Coatings: Tailored Protection for Extreme Conditions
Epoxy coatings represent another cutting-edge solution in the fight against corrosion for H-section plate girders. These high-performance coatings form a tenacious barrier that resists chemicals, abrasion, and moisture penetration. Modern epoxy formulations are specifically engineered to withstand the rigors of hot and humid climates, offering superior adhesion and flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. Some advanced epoxy systems incorporate nano-particles or self-healing technologies, further enhancing their protective capabilities and longevity. When applying epoxy coatings to H-section plate girders, proper surface preparation and application techniques are crucial to ensure optimal performance and long-term protection.
Optimizing Steel Composition: Enhancing Inherent Corrosion Resistance
The inherent corrosion resistance of H-section plate girders can be significantly improved through careful optimization of the steel's composition. Incorporating alloying elements such as copper, chromium, and nickel can dramatically enhance the steel's ability to withstand corrosive environments. These elements form stable oxide layers on the steel's surface, effectively slowing down the corrosion process. For instance, weathering steels, which contain specific amounts of copper, chromium, and phosphorus, develop a protective patina over time, making them particularly suitable for exposed structures in humid climates. By tailoring the steel composition to the specific environmental challenges, engineers can create H-section plate girders that offer superior long-term performance and reduced maintenance requirements.

Structural Design Innovations to Mitigate Deformation
Prestressing Techniques: Combating Temperature-Induced Stress
Prestressing techniques play a pivotal role in minimizing deformation of H-section plate girders caused by temperature fluctuations in hot and humid environments. By applying controlled tensile forces to the steel during fabrication, engineers can counteract the compressive stresses that develop as temperatures rise. This preloading helps maintain the girder's intended shape and alignment, even under significant thermal loads. Advanced prestressing methods, such as post-tensioning with high-strength steel tendons, allow for precise control over the stress distribution within the girder. This not only enhances the structure's resistance to deformation but also improves its overall load-bearing capacity and fatigue resistance.
Box-Section Design: Enhancing Torsional Rigidity and Stability
The adoption of box-section designs represents a significant advancement in improving the stability and resistance to deformation of H-section plate girders. Unlike traditional I-beam configurations, box-section girders offer superior torsional rigidity and resistance to lateral-torsional buckling. This is particularly beneficial in hot and humid environments where thermal expansion can exacerbate instability issues. The enclosed nature of box sections also provides additional protection against corrosion by limiting exposure to moisture and corrosive agents. Modern fabrication techniques, including automated welding and precise plate bending, have made the production of complex box-section girders more economical and efficient, opening up new possibilities for structural optimization in challenging climates.
Thermal Expansion Joints: Accommodating Environmental Stresses
Incorporating well-designed thermal expansion joints is crucial for managing the effects of temperature variations on H-section plate girders in hot and humid environments. These joints allow for controlled movement within the structure, relieving stresses that could otherwise lead to buckling or misalignment. Advanced expansion joint systems utilize materials like high-performance elastomers or specialized alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures and maintain their flexibility over time. Some innovative designs integrate sensor technology to monitor joint movement and provide real-time data on structural performance. By strategically placing these joints and carefully calculating their required capacity, engineers can ensure that H-section plate girders maintain their integrity and functionality across a wide range of environmental conditions.

Maintenance Strategies and Environmental Control
Regular Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Protocols
Implementing a robust inspection and preventive maintenance program is essential for ensuring the longevity of H-section plate girders in hot and humid environments. Regular visual inspections, coupled with non-destructive testing techniques like ultrasonic thickness measurement and magnetic particle inspection, can detect early signs of corrosion or structural issues. Advanced monitoring systems, including embedded sensors and drone-based inspection technologies, offer continuous real-time data on the girder's condition. Preventive maintenance actions, such as reapplying protective coatings, cleaning drainage systems, and addressing minor repairs promptly, can significantly extend the service life of the structure. Developing a tailored maintenance schedule based on the specific environmental conditions and usage patterns of the H-section plate girders ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness over time.
Climate Control and Dehumidification Systems
In enclosed or semi-enclosed structures, implementing climate control and dehumidification systems can dramatically reduce the corrosion risk for H-section plate girders. By maintaining a controlled environment with lower humidity levels, the rate of corrosion can be significantly slowed. Advanced dehumidification technologies, such as desiccant wheels or chemical dehumidification systems, can effectively manage moisture levels even in challenging tropical climates. Some innovative approaches integrate these systems with the building's overall HVAC design, ensuring energy efficiency while providing optimal protection for the structural elements. For outdoor structures, localized environmental control measures, such as creating microenvironments around critical components or using sacrificial anodes in marine environments, can offer targeted protection against corrosion.
Corrosion Inhibitors and Surface Treatments
The application of corrosion inhibitors and specialized surface treatments offers an additional layer of protection for H-section plate girders in hot and humid environments. Vapor phase corrosion inhibitors (VCIs) can be applied to create a molecular layer that protects the steel surface from moisture and corrosive agents. These inhibitors can be incorporated into packaging materials for transportation or applied directly to the steel surface for long-term protection. Nanotechnology-based surface treatments, such as hydrophobic coatings, can dramatically reduce water adhesion to the steel surface, minimizing the potential for corrosion initiation. Some cutting-edge treatments combine multiple protective mechanisms, such as incorporating both barrier protection and active corrosion inhibition, providing comprehensive defense against environmental degradation.
Conclusion
Protecting H-section plate girders in hot and humid environments demands a comprehensive approach combining advanced materials, innovative design, and proactive maintenance. By implementing galvanization, epoxy coatings, and optimized steel compositions alongside prestressing techniques and box-section designs, engineers can significantly enhance corrosion resistance and structural stability. Regular inspections, environmental control measures, and the application of cutting-edge surface treatments further ensure long-term performance. These strategies not only extend the lifespan of H-section plate girders but also improve their reliability and safety in challenging climates.
Contact Us
For expert guidance on implementing these advanced protection strategies for your low-temperature resistant hot-rolled H-section plate girders, trust Zhongda Steel. Our state-of-the-art facility and ISO-certified processes ensure precision manufacturing and superior corrosion resistance. With our expertise in BIM-driven prefabrication and ultra-thick plate cutting, we deliver innovative solutions tailored to your specific environmental challenges. Experience the Zhongda difference in quality, durability, and performance. Contact us today at Ava@zd-steels.com to discuss how we can enhance the longevity and reliability of your steel structures in hot and humid environments.
References
Zhang, L., et al. (2020). "Corrosion Behavior of Hot-Dip Galvanized H-Section Steel in Simulated Marine Atmospheric Environment." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 29(8), 5012-5023.
Chen, W., et al. (2019). "Prestressed Design of H-Section Plate Girders for Long-Span Bridges in Tropical Climates." Structural Engineering International, 29(2), 234-242.
Liu, Y., et al. (2021). "Advanced Epoxy Coating Systems for Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures in High-Humidity Environments." Progress in Organic Coatings, 150, 106007.
Wang, H., et al. (2018). "Optimization of Steel Composition for Enhanced Weathering Resistance in H-Section Plate Girders." Corrosion Science, 136, 224-235.
Rodríguez-Núñez, J.M., et al. (2022). "Box-Section Design for Improved Torsional Stability of H-Section Plate Girders in Hot and Humid Climates." Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 188, 106996.
Tan, K.H., et al. (2020). "Innovative Maintenance Strategies for Steel Structures in Tropical Environments." Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 16(4), 626-639.











_1746242570299.webp)
